Osteopathy
What Is Osteopathy?
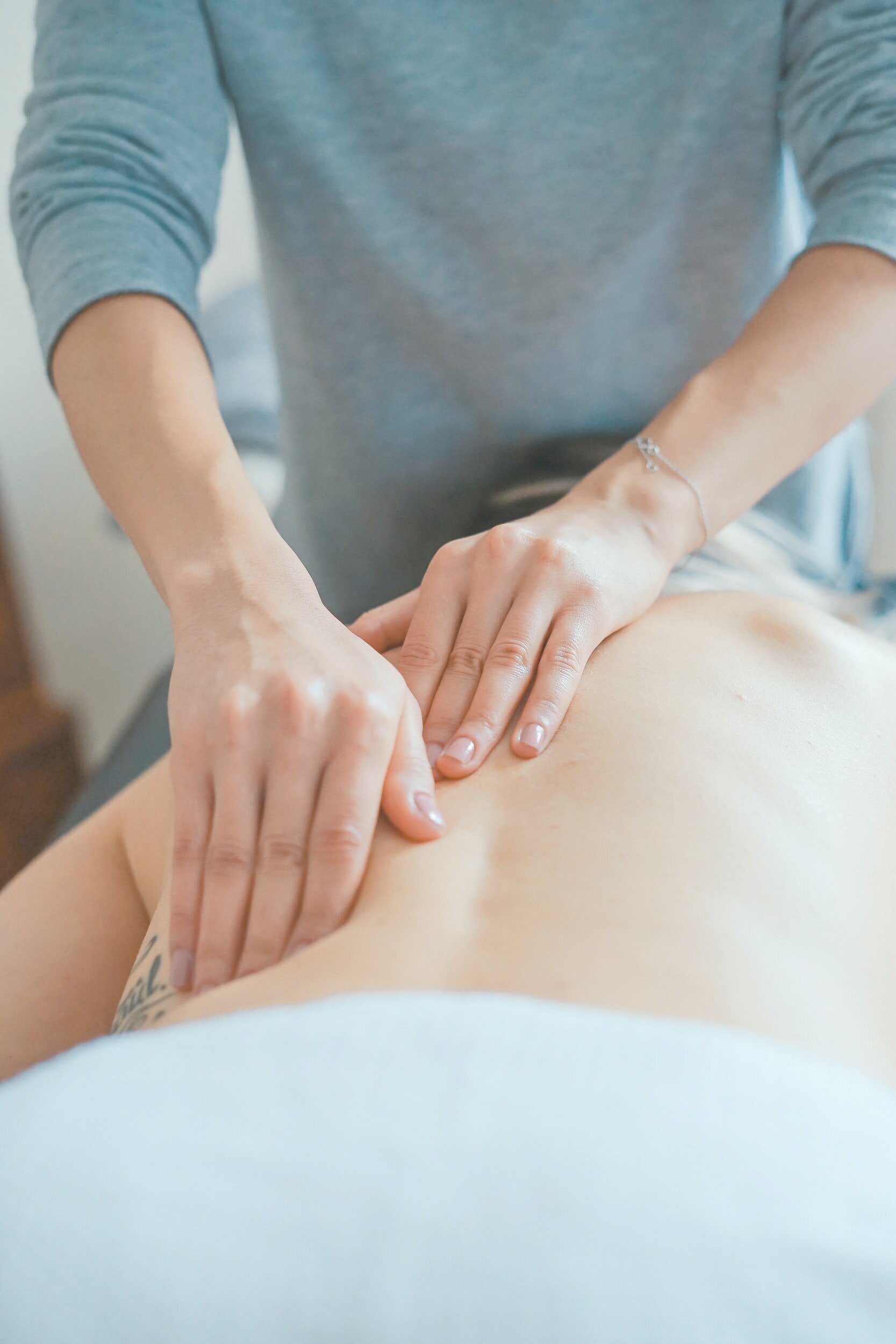
Osteopathy is a non-invasive form of manual medicine which focuses on the health of the whole body, recognising the important relationship between the structure of the body and how it functions as a unit.
Osteopathic practitioners are primary health care providers that help the body to facilitate its own healing mechanisms by rebalancing the musculoskeletal system, connective tissues, nerves, circulation and internal organs.
Osteopathy can be used to assist with a wide range of conditions and is gentle, safe and effective for everyone from babies through to the elderly, to pregnant women, and people with acute or chronic conditions.
Common complaints that osteopaths treat include (but are not limited to) neck and back pain, headaches, sport and work-related injuries, and other joint or muscular issues.
Osteopathy can also assist with breathing and digestive complaints, and help relieve aches and pains associated with pregnancy and post-partum by working with the associated musculoskeletal components.
Osteopaths identify important types of dysfunction through skilled evaluation and diagnosis and provide treatment using a variety of hands-on direct (structural) and in-direct (cranial) techniques.
Structural techniques include stretching and massage of the soft tissues (muscles, tendons and ligaments), along with gentle mobilisation, articulation and manipulation of specific joints and soft tissues.
Cranial osteopathy is applied through very light touch to identify and release subtle tension, strains and imbalances throughout the whole body and its systems. It is especially effective and beneficial for babies and children as their bones are still very soft, allowing them to be very responsive to this style treatment.
What Do Osteopaths Commonly Treat?
General Aches & Pains
Neck & Back Pain
Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist & Hand Pain
Hip, Knee, Ankle & Foot Pain
Postural Tension & Stiffness
Delayed-onset Muscle Soreness
Preventative/Maintenance Care
Accidents & Injuries
Work-related Injuries
OOS, RSI, Repetitive Strains
Sporting Injuries
Concussion & Trauma
Post-surgical Rehabilitation
Specific Conditions
Headaches & Migraines
Pregnancy & Post-partum
TMJ & Facial Pain
Anxiety & Stress-related
Asthma & Breathing
Digestive Problems
Pelvic Pain & Sciatica
Joint Pain & Arthritis
What Training Do Osteopaths Have?
Osteopaths are registered health practitioners and ACC providers that are regulated through the Osteopathic Council of New Zealand (OCNZ).
Osteopaths receive 4 or 5 years of university training obtaining a Bachelor of Applied Science (Human Biology) and Master of Osteopathy (or equivalent qualification depending on training institution).
Any osteopaths who have trained overseas will have had their training assessed and approved to be of the same standard by OCNZ.
Osteopathic training covers all of the medical sciences with a focus on osteopathic principles, diagnosis, treatment and management of musculoskeletal conditions.
A referral is not required to see an osteopath as osteopaths have the training, knowledge and skills to identify if any further investigation may be required or if your condition is outside of our scope of practice.
If further investigation is required or your condition is outside our scope of treatment we can explain this and refer you for X-rays, ultrasounds and further specialist care.
In order to maintain a practicing certificate osteopaths must complete a set number of continuing professional development hours. This helps us to stay up-to-date with the latest research and continue to develop our skillset as practitioners.
Testimonials